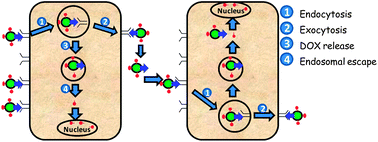
We report that receptor mediated transcytosis can be utilized to facilitate tumor penetration by drug loaded nanoparticles (NPs). We synthesized hyaluronan (HA) coated silica nanoparticles (SNPs) containing a highly fluorescent core to target CD44 expressed on the cancer cell surface. Although prior studies have primarily focused on CD44 mediated endocytosis to facilitate cellular uptake of HA-NPs by cancer cells, we discovered that, once internalized, the HA-SNPs could be transported out of the cells with their cargo. The exported NPs could be taken up by neighboring cells. This enabled the HA-SNPs to penetrate deeper inside tumors and reach a much greater number of tumor cells in 3D tumor models, presumably through tandem cycles of CD44 mediated endocytosis and exocytosis. When doxorubicin (DOX) was loaded onto the NPs, better penetration of multilayered tumor cells was observed with much improved cytotoxicities against both drug sensitive and drug resistant cancer spheroids compared to the free drug. Thus, targeting receptors such as CD44 that can readily undergo recycling between the cell surface and interior of the cells can become a useful strategy to enhance the tumor penetration potential of NPs and the efficiency of drug delivery through receptor mediated transcytosis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...