Managing voids of Si anodes in lithium ion batteries
Abstract
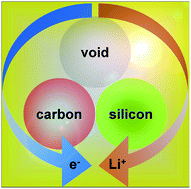
The implementation of silicon (Si) in practical lithium ion battery electrodes has been hindered due to its large volume change and consequent structural and interfacial instabilities. Coating nanostructured Si with a second phase (e.g., carbon (C)) represents a very promising strategy for dealing with these critical issues facing Si-based electrodes. In this review article, we will outline recent advances in coating Si with engineered C matrices. By exemplifying hollow core–shell, core–hollow shell, and core–shell structured Si–C hybrid nanomaterials, we aim to highlight the importance of managing voids in designing such Si–C hybrid electrodes, and provide some scientific insights into the development of advanced Si-based anodes for next-generation lithium ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...