Three dimensional quantitative characterization of magnetite nanoparticles embedded in mesoporous silicon: local curvature, demagnetizing factors and magnetic Monte Carlo simulations†
Abstract
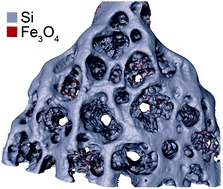
Magnetite nanoparticles embedded within the pores of a mesoporous silicon template have been characterized using electron tomography. Linear least squares optimization was used to fit an arbitrary ellipsoid to each segmented particle from the three dimensional reconstruction. It was then possible to calculate the demagnetizing factors and the direction of the shape anisotropy easy axis for every particle. The demagnetizing factors, along with the knowledge of spatial and volume distribution of the superparamagnetic nanoparticles, were used as a model for magnetic Monte Carlo simulations, yielding zero field cooling/field cooling and magnetic hysteresis curves, which were compared to the measured ones. Additionally, the local curvature of the magnetite particles' docking site within the mesoporous silicon's surface was obtained in two different ways and a comparison will be given. A new iterative semi-automatic image alignment program was written and the importance of image segmentation for a truly objective analysis is also addressed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...