One-step solvothermal synthesis of highly water-soluble, negatively charged superparamagnetic Fe3O4 colloidal nanocrystal clusters†
Abstract
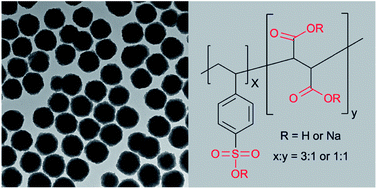
Highly charged hydrophilic superparamagnetic Fe3O4 colloidal nanocrystal clusters with an average diameter of 195 nm have been successfully synthesized using a modified one-step solvothermal method. Anionic polyelectrolyte poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) sodium salt containing both sulfonate and carboxylate groups was used as the stabilizer. The clusters synthesized under different experimental conditions were characterized with transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering; it was found that the size distribution and water dispersity were significantly affected by the concentration of the polyelectrolyte stabilizer and iron sources in the reaction mixtures. A possible mechanism involving novel gel-like large molecular networks that confined the nucleation and aggregation process was proposed and discussed. The colloidal nanocrystal clusters remained negatively charged in the experimental pH ranges from 2 to 11, and also showed high colloidal stability in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and ethanol. These highly colloidal stable superparamagnetic Fe3O4 clusters could find potential applications in bioseparation, targeted drug delivery, and photonics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...