The protonation state of trans axial water molecule switches: the reactivity of high-valent manganese-oxo porphyrin†
Abstract
The cationic manganese porphyrin (Mn-TMPyP) was activated by an oxygen atom donor KHSO5 (oxone) to form a high-valent manganese-oxo species (MnV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) in aqueous buffer. The high-valent MnV
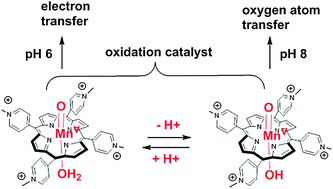
O) in aqueous buffer. The high-valent MnV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O mediated oxidative damage of short double-stranded DNA models. The nature of the oxidation products (guanine oxidation DGh, 2Ih, imidazolone, and 2-deoxyribose oxidation, 2-deoxyribonolactone) and the mechanism of their formation varied with the pH of the reaction. Oxidation proceeded mainly through the electron transfer mechanism at pH 6 while oxygen atom transfer proved to be favored at pH 8. This was evidenced by different ratios of products arising from different mechanisms of oxidation as a function of pH but also by different mechanisms leading to the same oxidation product (DGh) as a function of pH. The reactivity shift of the active manganese-oxo species was attributed to the protonation state of the proximal water molecule as an axial ligand (trans to the oxo). A high-valent manganese-oxo in the oxo-hydroxo form (HO–MnV
O mediated oxidative damage of short double-stranded DNA models. The nature of the oxidation products (guanine oxidation DGh, 2Ih, imidazolone, and 2-deoxyribose oxidation, 2-deoxyribonolactone) and the mechanism of their formation varied with the pH of the reaction. Oxidation proceeded mainly through the electron transfer mechanism at pH 6 while oxygen atom transfer proved to be favored at pH 8. This was evidenced by different ratios of products arising from different mechanisms of oxidation as a function of pH but also by different mechanisms leading to the same oxidation product (DGh) as a function of pH. The reactivity shift of the active manganese-oxo species was attributed to the protonation state of the proximal water molecule as an axial ligand (trans to the oxo). A high-valent manganese-oxo in the oxo-hydroxo form (HO–MnV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) at higher pH undergoes oxygen atom transfer reactions while in the oxo-aqua form (H2O–MnV
O) at higher pH undergoes oxygen atom transfer reactions while in the oxo-aqua form (H2O–MnV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) at lower pH it performs oxidation reactions by electron transfer. These data are an illustration of the influence of the “push” effect of the proximal ligand on the changing reactivity of high-valent metal-oxo species. They also give access to the pKa of the axially bound water molecule of manganese-oxo porphyrin.
O) at lower pH it performs oxidation reactions by electron transfer. These data are an illustration of the influence of the “push” effect of the proximal ligand on the changing reactivity of high-valent metal-oxo species. They also give access to the pKa of the axially bound water molecule of manganese-oxo porphyrin.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of Bernard Meunier

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...