One-pot template-free synthesis of water-dispersive Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for adsorption of bovine serum albumin
Abstract
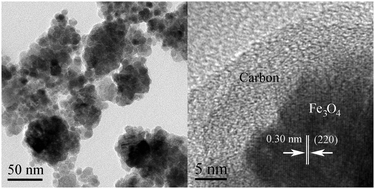
Water-dispersive Fe3O4@C nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized on a large scale via a one-pot template-free solvothermal process. The core–shell structure of the product was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) of the sample indicated that abundant amide carbonyl groups are formed on the surface of the Fe3O4@C nanoparticles. Based on the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) results, the contents of Fe3O4 and carbon are calculated to be 77.5% and 6.1%, respectively. Magnetic measurements illustrated that the prepared composites are superparamagnetic magnets with a saturation magnetization of 69.2 emu g−1. Because of their hydrophilic core–shell structure, the prepared Fe3O4@C nanoparticles show a high bovine serum albumin (BSA) protein adsorption capacity (82.78 mg g−1) and a fast adsorption rate (60 min) in aqueous solutions. This work demonstrates that the prepared magnetic nanoparticles have promising applications in enzyme and protein immobilization.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...