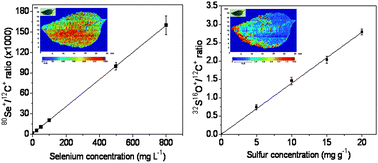
Qualitative and quantitative methods were developed for selenium and sulphur mapping/quantification in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) leaves. The plants were grown for 50 days in a greenhouse, being divided into two groups, one irrigated with only deionized water and the other treated with a daily dose of 7.58 mg of Na2SeO3. Leaves were collected during the growth period for directly evaluating the distribution of Se and S in these structures. For quantification analysis, pellets were produced from both CRM (100 and 1575a for Se and S, respectively) and the sunflower materials. The pellets were doped with 25 and 1200 μg g−1 Se and 5 and 20 mg g−1 S and analyzed by LA-ICP-MS. For accuracy purposes all the samples were also decomposed via microwave and analyzed by ICP-MS. To avoid polyatomic interferences Se and S were monitored as SeO+ and SO+ at m/z 96 and 48, respectively, 12C+ was used as an internal standard, and the ratios between SeO+/C+ and SO+/C+ were used for measurements. Statistic tests (t test at 95% confidence level) confirming good agreement between LA-ICP-MS and ICP-MS indicated the accuracy of this technique.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...