Exploring the structural determinants of selective phosphopeptide recognition using bivalent metal-coordination complexes†
Abstract
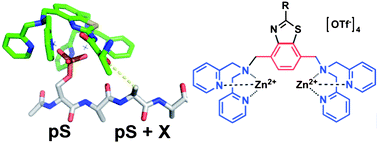
We herein explore the structural determinants of selective phosphopeptide recognition by employing novel bivalent, bis-(Zn2+-dipicolylamine)-based coordination complexes against a select library of model phosphoserine-containing peptides of varying amino acid composition. The results demonstrated that Lewis acidic coordination complexes equipped with cationic binding groups might be best utilized as selective receptors for binding phosphopeptides with anionic side chain residues proximal to the phosphoserine residue.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...