Antimicrobial medical sutures with caffeic acid phenethyl ester and their in vitro/in vivo biological assessment
Abstract
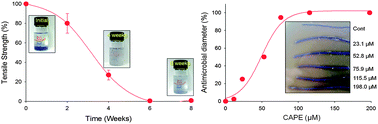
The work report the in vitro and in vivo assessment of antimicrobial poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) sutures loaded with noble natural extracts, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) from natural propolis. The mechanical characteristics of the medical sutures have been elucidated including tensile strength as a function of biodegradability, and the sustained release profile of CAPE on sutures has been measured as a function of time, concentration and optimization with the aim of maximizing their antimicrobial effect against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia DH5α bacteria. Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial assessments – cytotoxicity tests, bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assays, and micronucleus assays – were achieved to investigate biocompatibility. Real time RT-PCR showed that the antimicrobial effect of CAPE is related to outer membrane damage and
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...