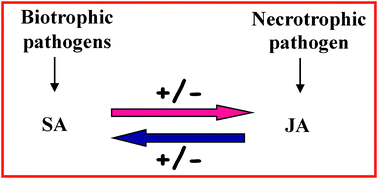
Resistance conferred by biotrophic pathogens often requires salicylic acid (SA) signaling, whereas necrotrophic pathogens or wounding mainly activate the jasmonate/ethylene (JA/ET)-dependent pathway. Crosstalk connections between these two independent signaling pathways may lead to synergistic or antagonistic behavior. In order to shed some light on the crosstalk between these two hormones in Arabidopsis plants, a proteomic approach combined with a transcriptomic analysis has been used to identify molecules differentially expressed upon single or simultaneous treatment with both phytohormones. Twenty-five nonredundant differential proteins were revealed upon treatment with SA or JA alone or in combination, which are involved in general metabolic processes as well as in response to stress, in developmental processes, in protein metabolism and transport. Interestingly, gene expression study, carried out on genes involved in oxidative stress and in biotic and/or abiotic stress, highlighted the correspondence between proteomic and transcriptomic approaches, performed here by RT-PCR. Our data clearly demonstrate that almost all genes/proteins involved in oxidative stress as well as in biotic and/or abiotic stress are mainly induced upon JA treatment and only a few of them are overexpressed upon SA treatment. Moreover, we found that a substantially negative crosstalk is established upon the combined action of the two hormones and that generally SA exerts a negative crosstalk compared to the JA pathway. Our study corroborates the hypothesis that the combination of both phytohormones induces reprogramming of the plant transcriptome, but at the same time highlights the presence of a complex network of signaling that is far to be completely elucidated.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...