Interaction of AnxA6 with isolated and artificial lipid microdomains; importance of lipid composition and calcium content
Abstract
Niemann-Pick type C (
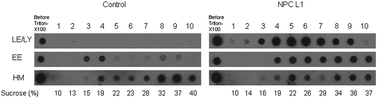
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Biochemistry, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, 3 Pasteur Street, 02-093 Warsaw, Poland
E-mail:
s.pikula@nencki.gov.pl
Fax: +48 22 822 5342
b ICBMS, UMR CNRS 5246, CPE Lyon, INSA Lyon, Université Claude Bernard Lyon1, 43 Boulevard du 11 Novembre 1918, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
c Clinic of Metabolic Diseases, Endocrinology and Diabetology, The Children's Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw, Poland
Niemann-Pick type C (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. M. Domon, F. Besson, A. Tylki-Szymanska, J. Bandorowicz-Pikula and S. Pikula, Mol. BioSyst., 2013, 9, 668 DOI: 10.1039/C3MB25487A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
