Innate immunomodulation by lipophilic termini of lipopolysaccharide; synthesis of lipid As from Porphyromonas gingivalis and other bacteria and their immunomodulative responses†
Abstract
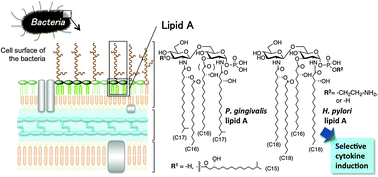
Synthetic studies of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Biosystems Chemical Biology in Asia

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...