A microfluidic device for dry sample preservation in remote settings†
Abstract
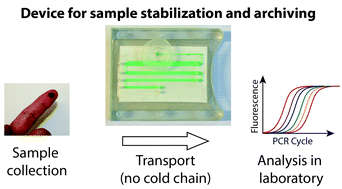
This paper describes a microfluidic device for dry preservation of biological specimens at room temperature that incorporates chemical stabilization matrices. Long-term stabilization of samples is crucial for remote medical analysis, biosurveillance, and archiving, but the current paradigm for transporting remotely obtained samples relies on the costly “cold chain” to preserve analytes within biospecimens. We propose an alternative approach that involves the use of microfluidics to preserve samples in the dry state with stabilization matrices, developed by others, that are based on self-preservation chemistries found in nature. We describe a SlipChip-based device that allows minimally trained users to preserve samples with the three simple steps of placing a sample at an inlet, closing a lid, and slipping one layer of the device. The device fills automatically, and a pre-loaded desiccant dries the samples. Later, specimens can be rehydrated and recovered for analysis in a laboratory. This device is portable, compact, and self-contained, so it can be transported and operated by untrained users even in limited-resource settings. Features such as dead-end and sequential filling, combined with a “pumping lid” mechanism, enable precise quantification of the original sample’s volume while avoiding overfilling. In addition, we demonstrated that the device can be integrated with a plasma filtration module, and we validated device operations and capabilities by testing the stability of purified RNA solutions. These features and the modularity of this platform (which facilitates integration and simplifies operation) would be applicable to other microfluidic devices beyond this application. We envision that as the field of stabilization matrices develops, microfluidic devices will be useful for cost-effectively facilitating remote analysis and biosurveillance while also opening new opportunities for diagnostics, drug development, and other medical fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...