Simple, distance-based measurement for paper analytical devices
Abstract
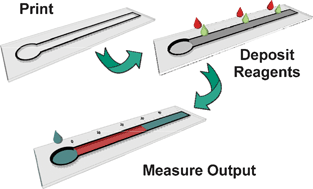
Paper-based analytical devices (PADs) represent a growing class of elegant, yet inexpensive chemical sensor technologies designed for point-of-use applications. Most PADs, however, still utilize some form of instrumentation such as a camera for quantitative detection. We describe here a simple technique to render PAD measurements more quantitative and straightforward using the distance of colour development as a detection motif. The so-called distance-based detection enables PAD chemistries that are more portable and less resource intensive compared to classical approaches that rely on the use of peripheral equipment for quantitative measurement. We demonstrate the utility and broad applicability of this technique with measurements of glucose, nickel, and glutathione using three different detection chemistries: enzymatic reactions, metal complexation, and nanoparticle aggregation, respectively. The results show excellent quantitative agreement with certified standards in complex sample matrices. This work provides the first demonstration of distance-based PAD detection with broad application as a class of new, inexpensive sensor technologies designed for point-of-use applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...