A microfluidic system for cell type classification based on cellular size-independent electrical properties
Abstract
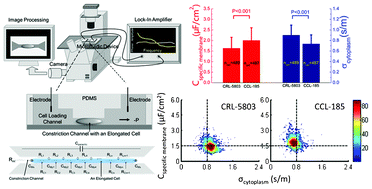
This paper presents a microfluidic system enabling cell type classification based on continuous characterization of size-independent electrical properties (e.g., specific membrane capacitance (Cspecific membrane) and cytoplasm conductivity (σcytoplasm)). In this study, cells were aspirated continuously through a constriction channel, while cell elongation and impedance profiles at two frequencies (1 kHz and 100 kHz) were measured simultaneously. Based on a proposed distributed equivalent circuit model, 1 kHz impedance data were used to evaluate cellular sealing properties with constriction channel walls and 100 kHz impedance data were translated to Cspecific membrane and σcytoplasm. Two lung cancer cell lines of CRL-5803 cells (ncell = 489) and CCL-185 cells (ncell = 487) were used to evaluate this technique, producing a Cspecific membrane of 1.63 ± 0.52 μF cm−2vs. 2.00 ± 0.60 μF cm−2, and σcytoplasm of 0.90 ± 0.19 S m−1vs. 0.73 ± 0.17 S m−1. Neural network-based pattern recognition was used to classify CRL-5803 and CCL-185 cells, producing success rates of 65.4% (Cspecific membrane), 71.4% (σcytoplasm), and 74.4% (Cspecific membrane and σcytoplasm), suggesting that these two tumor cell lines can be classified based on their electrical properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...