Biocomposite of nanostructured MnO2 and fique fibers for efficient dye degradation†
Abstract
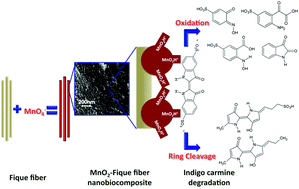
We report on the in situ synthesis of nanostructured MnO2 onto natural fique fibers. The fiber surface was rendered positive by exposure to alkaline conditions, and permanganate anions (MnO4−) were embedded onto the resultant alkali cellulose via coulombic interactions. An ultrasound-assisted procedure was used to reduce MnO4− and yield MnO2 nanoparticles (NPs). UV-Vis diffuse reflectance was used to assess the influence of the precursor concentration, loading and reduction times on the synthesis of the nanostructured MnO2. FESEM provided direct evidence that MnO2 NPs and aggregates could be formed on the fiber's surface. The catalytic activity of the new bionanocomposite was tested for the removal of indigo carmine dye in water samples. The MnO2–fique fiber bionanocomposite was able to remove up to 98% of the colour present in the contaminated water samples in less than 5 minutes. Mass spectrometry was used to determine the degradation route of the dye. Additionally, we found that the bionanocomposite can be reused with no effect on the dye degradation efficiency. The reported procedure provides a new route for the development of biodegradable and easy to synthesize composite materials capable of efficiently degrading pollutants found in industrial effluents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...