Unusual reactions mediated by FMN-dependent ene- and nitro-reductases
Abstract
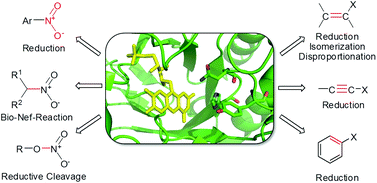
Due to the chemical versatility of the flavin cofactor, FMN-dependent ene-reductases and nitro-reductases can catalyze or mediate a diverse spectrum of chemical reactions. Among them, two-electron transfer reactions dominate, which may proceed via sequential hydride transfer at the same or at alternate reactive sites. In addition, highly reactive intermediates are often formed, which undergo subsequent spontaneous (non-enzymatic) reactions leading to further enzymatic transformations in a cascade. Besides the well-known reductive processes involving alkenes and nitro groups at the expense of a reduced flavin cofactor, redox-neutral processes including disproportionation and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C-bond isomerization reactions are catalyzed by OYE homologues. Unusual flavin-dependent biotransformations are reviewed with a special focus on the OYE family of flavoproteins (ene-reductases) and oxygen-insensitive FMN-dependent nitro-reductases.
C-bond isomerization reactions are catalyzed by OYE homologues. Unusual flavin-dependent biotransformations are reviewed with a special focus on the OYE family of flavoproteins (ene-reductases) and oxygen-insensitive FMN-dependent nitro-reductases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...