Antioxidant effect of salidroside and its protective effect against furan-induced hepatocyte damage in mice
Abstract
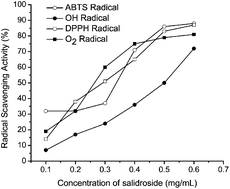
Furan, a widely used industrial compound, has been found in many heat-treated foods, especially baby food. The presence of furan in food raises concerns about public health. In this study, we evaluated the protective effect of salidroside (SR) against furan-induced hepatocyte damage in mice livers. The in vitro antioxidant effects of SR were also evaluated. The results suggested that furan significantly increased hepatocyte damage, as proven by the increased activities of aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and levels of direct bilirubin (DBIL). Furan also caused oxidative stress, as evidenced by increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production as well as malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and glutathione S-transferase (GST) activity in mice livers. Pretreatment with SR markedly attenuated the activities of AST, ALT, GST and the levels of DBIL, ROS, and MDA in a dose-dependent manner. The protective effects of SR against furan-induced hepatocyte damage were due to its excellent ability to scavenge free radicals such as 2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) radicals, ˙OH, 2,2-di(4-tert-octylphenyl)-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals and ˙O2−. Thus, SR exerted excellent antioxidant effects, and it may be a novel therapeutic and preventive agent for oxidative stress-related diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...