Use of a highly sensitive recombinant hepatoma cell method to determine dioxin concentrations in samples of fish and crab from a hotspot area†
Abstract
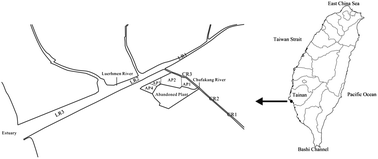
A new and easy fast-screening test (the Ad-DR (adenoviral vector-dioxin response) bioassay) for dioxins in biological samples from highly dioxin-contaminated areas was developed. The aryl-hydrocarbon-receptor (AhR) reporter system was utilized to transport a dioxin-responsive-element (DRE) via an adenovirus vector into rat hepatoma (H4IIE) cells before each experiment; these DRE-H4IIE cells were utilized in the Ad-DR bioassay. Biological extracts were simultaneously analyzed by the Ad-DR bioassay and high resolution

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...