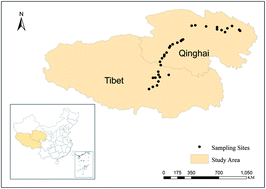
Thirty four sampling sites along an elevation transect in the Tibetan Plateau region were chosen. Soil cores were divided into several layers and a total of 175 horizon soil samples were collected from July to September 2011, for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The measured PAHs concentration in surface soils was 56.26 ± 45.84 ng g−1, and the low molecular weight PAHs (2–3 rings) predominated, accounting for 48% and 35%. We analyzed the spatial (altitudinal and vertical) distribution of PAHs in soil, and explored the influence of related environmental factors. Total organic carbon (TOC) showed a controlling influence on the distribution of PAHs. PAH concentrations declined with soil depth, and the composition patterns of PAHs along soil depth indicated that the heavy PAHs tended to remain in the upper layers (0–10 cm), while the light fractions were transported downward more easily. PAHs inventories (8.77–57.92 mg m−2) for soil cores increased with mean annual precipitation, while the topsoil concentrations decreased with it. This implies that an increase in precipitation could transfer more PAHs from the atmosphere to the soil and further transport PAHs from the topsoil to deeper layers.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...