A carbon quantum dot decorated RuO2 network: outstanding supercapacitances under ultrafast charge and discharge
Abstract
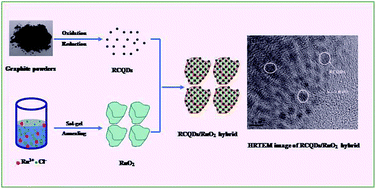
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) due to their unique properties have recently attracted extensive attention from researchers in many fields. In the present work, a new application in the form of a CQD-based hybrid as an excellent electrode material for supercapacitors is reported for the first time. The CQDs are fabricated by a facile chemical oxidation method following which they are thermally reduced, and further decorated with RuO2 to obtain the composites. The hybrid exhibits a specific capacitance of 460 F g−1 at an ultrahigh current density of 50 A g−1 (41.9 wt% Ru loading), and excellent rate capability (88.6, 84.2, and 77.4% of capacity retention rate at 10, 20, and 50 A g−1 compared with 1 A g−1, respectively). Surprisingly, the hybrid shows exceptional cycling stability with 96.9% capacity retention over 5000 cycles at 5 A g−1. Such remarkable electrochemical performances can be primarily ascribed to the significantly enhanced utilization of RuO2 achieved by the efficient dispersion of tiny reduced CQDs and the formation of a CQD-based hybrid network structure that can facilitate the fast charge transport and ionic motion during the charge–discharge process. Additionally, the contact resistance at the interface between active materials and current collectors is concluded to be a key factor in determining the performance of the hybrid. These results above demonstrate the great potential of CQD-based hybrid materials in the development of high-performance electrode materials for supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...