Charge photo-accumulation and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light at an iridium(iii)-photosensitized polyoxotungstate†‡
Abstract
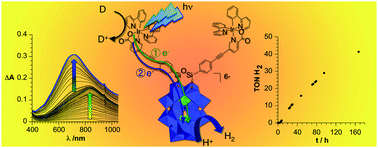
Steady-state irradiation under visible light of a covalent Ir(III)-photosensitized polyoxotungstate is reported. In the presence of a sacrificial electron donor, photolysis leads to a very efficient photoreduction of the polyoxometalate. Successive formation of the one-electron and two-electron reduced species, which are unambiguously identified by comparison with spectroelectrochemical measurements, is observed with a significantly faster rate reaction for the formation of the one-electron reduced species. The kinetics of the photoreduction, which are correlated with the reduction potentials of the polyoxometalate (POM), can be finely tuned by the presence of an acid. Indeed light-driven formation of the two-electron reduced POM is considerably facilitated in the presence of acetic acid. The system is also able to perform photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light without significant loss of performance over more than 1 week of continuous photolysis and displays higher photocatalytic efficiency than the related multi-component system, outlining the decisive effect of the covalent bonding between the POM and the photosensitizer. This functional and modular system constitutes a promising step for the development of charge photoaccumulation devices and subsequent photoelectrocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...