Sensitive and selective detection of cesium via fluorescence quenching†
Abstract
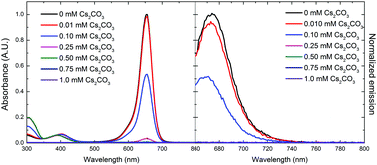
Herein we report a robust and easy method for detecting cesium metal ion (Cs+) in partially aqueous solutions using the fluorescence quenching of 2,4-bis[4-(N,N-dihydroxyethylamino)phenyl]squaraine. This squaraine dye was found to be both highly sensitive (low limits of detection) and selective (limited response to other metals) for cesium ion detection. The detection is likely based on the metal complexing to the dihydroxyethanolamine moieties, which disrupts the donor–acceptor–donor architecture and leads to efficient quenching.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...