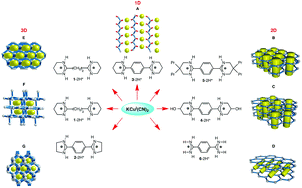
Upon combining KCu(CN)2 with six different symmetrical dicationic bisamidinium moieties possessing different shapes and geometries, seven new coordination networks of the cyanocuprate type displaying 1-, 2- and 3-D dimensionality have been obtained. The formation of networks results from the interconnection of Cu(I) centres by cyanide anions through different bridging modes. The organic dicationic tectons interact with the anionic networks by charge-assisted H-bonds and, depending on their geometric features, they play different structuring roles. In the case of the 1D cyanocuprate networks, the organic cation interconnects consecutive anionic chains, increasing thus the overall dimensionality of the arrangement to 2D. For the 2D networks, either riveting or intercalation has been observed. For the riveting case, either the process takes place only between two consecutive sheets leading to a double layer type arrangement and thus without an increase of dimensionality, or between consecutive 2D networks in an alternate fashion. In the latter case, the dimensionality of the overall architecture is increased to 3 as for the intercalated case. For the 3D architectures, the dicationic moieties are located within the generated channels.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...