Controlled synthesis of Au-loaded Fe3O4@C composite microspheres with superior SERS detection and catalytic degradation abilities for organic dyes†
Abstract
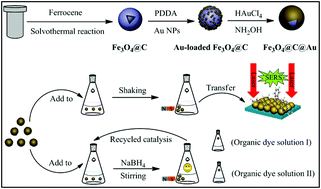
Bifunctional Au-loaded Fe3O4@C composite microspheres were controllably synthesized by coating of Au

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...