The influence of RAPTA moieties on the antiproliferative activity of peripheral-functionalised poly(salicylaldiminato) metallodendrimers†
Abstract
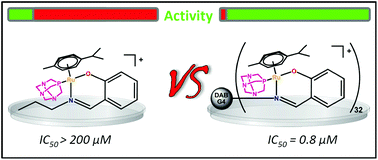
Cationic N,O-chelating dendrimers functionalised on the periphery with RAPTA-like (ruthenium(II)-arene-1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.1]decane) moieties have been synthesised and characterised using NMR and IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis and MALDI-TOF/HR-ESI mass spectrometry. Metallodendrimers from the first to the fourth-generation containing up to 32 peripheral ruthenium-arene-PTA moieties were obtained. Model mononuclear analogues, [{Ru(η6-p-cymene)((C7H5NO)-κ2-N,O)(PTA)}((CH2)3)][PF6] and [{Ru(η6hexamethylbenzene)((C7H5NO)-κ2-N,O)(PTA)}((CH2)3)][PF6], have been prepared and their structures were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The cytotoxicities of the metallodendrimers and their mononuclear analogues were established on A2780 and A2780cisR human ovarian carcinoma cancer cells and model human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...