Mesostructured Co–Ce–Zr–Mn–O composite as a potential catalyst for efficient removal of carbon monoxide from hydrogen-rich stream†
Abstract
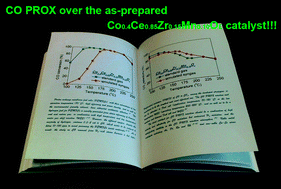
Mesostructured CoxCe0.85Zr0.15MnyOε composites were firstly prepared by a simple one-pot
* Corresponding authors
a
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Catalysis Chemistry and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2 Linggong Road, Dalian 116024, China
E-mail:
zkzhao@dlut.edu.cn
b Key Laboratory of Oil & Gas Fine Chemicals, Ministry of Education & Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, Xinjiang 830046, China
Mesostructured CoxCe0.85Zr0.15MnyOε composites were firstly prepared by a simple one-pot

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Z. Zhao, R. Jin, Y. Li, Y. Dai and T. Muhammad, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3, 2130 DOI: 10.1039/C3CY00154G
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
