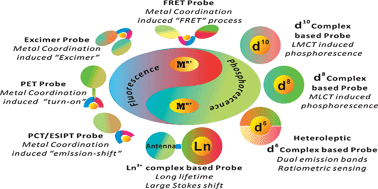
Coordination chemistry plays an essential role in the design of photoluminescent probes for metal ions. Metal coordination to organic dyes induces distinct optical responses which signal the presence of metal species of interest. Luminescent lanthanide (Ln3+) and transition metal complexes of d6, d8 and d10 configurations often exhibit unique luminescence properties different from organic dyes, such as high quantum yield, large Stokes shift, long emission wavelength and emission lifetimes, low sensitivity to microenvironments, and can be explored as lumophores to construct probes for metal ions, anions and neutral species. In this review, the design principles and coordination chemistry of metal probes based on mechanisms of PeT, PCT, ESIPT, FRET, and excimer formation will be discussed in detail. Particular attention will be given to rationales for the design of turn-on and ratiometric probes. Moreover, phosphorescent probe design based on Ln3+ and d6, d8 and d10-metal complexes are also presented via discussing certain factors affecting the phosphorescence of these metal complexes. A survey of the latest progress in photoluminescent probes for identification of essential metal cations in the human body or toxic metal cations in the environment will be presented focusing on their design rationales and sensing behaviors. Metal complex-based photoluminescent probes for biorelated anions such as PPi, and neutral biomolecules ATP, NO, and H2S will be discussed also in the context of their metal coordination-related sensing behaviors and design approaches.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...