Thermodynamically destabilized hydride formation in “bulk” Mg–AlTi multilayers for hydrogen storage†
Abstract
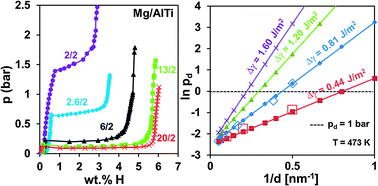
Thermodynamic destabilization of MgH2 formation through interfacial interactions in free-standing Mg–AlTi multilayers of overall “bulk” (0.5 μm) dimensions with a hydrogen capacity of up to 5.5 wt% is demonstrated. The interfacial energies of Mg–AlTi and Mg–Ti (examined as a baseline) are calculated to be 0.81 and 0.44 J m−2. The enhanced interfacial energy of AlTi opens the possibility of creating ultrathin alloy interlayers that provide further thermodynamic improvements in

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...