Effective bulk and surface temperatures of the catalyst bed of FT-IR cells used for in situ and operando studies
Abstract
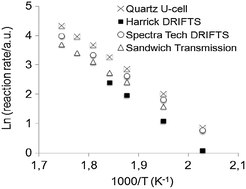
The temperature prevailing in the catalyst bed of three different IR spectroscopic reaction cells was assessed by means of thermocouples, an optical pyrometer and reaction rate measurements. One of the cells was a custom-made transmission FT-IR cell for use with thin wafers and the two others were commercial Harrick and Spectra-Tech diffuse reflectance FT-IR (DRIFTS) cells used for the analysis of powdered samples. The rate of CO methanation measured over a 16 wt% Ni/alumina catalyst was used as a means to derive the effective temperature prevailing in the IR cells from that existing in a traditional (non-spectroscopic) reactor having a well-controlled temperature. The sample bed of these three IR cells exhibited a significantly lower temperature than that of the corresponding measure thermocouple, which was yet located in or close to the sample bed. The comparison of Arrhenius plots enabled us to determine a temperature correction valid over a large temperature range. The use of an optical pyrometer was assessed with a view to determining the temperature of the surface of the powdered beds and that at the centre of the wafer. The optical pyrometer proved useful in the case of the catalyst powder, which behaved as a black non-reflecting body. In contrast, the temperature reading was inaccurate in the case of the pressed wafer, probably due to the shiny surface and minute thickness of the wafer, which led to a significant portion of the IR radiation of the surroundings being reflected by and transmitted through the wafer. The optical pyrometer data showed that the temperature of the surface of the powdered beds was significantly lower than that of the bulk of the bed, and that the total flow rate and composition did not affect this value. This work emphasises that the effective bed temperature in spectroscopic cells can be significantly different from that given by measure thermocouples, even when located in the vicinity of the sample, but that the calibration curves derived from rate measurements can be used to overcome this problem.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...