Abstract
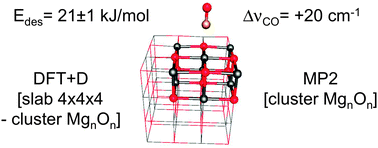
A hybrid MP2:DFT + D optimization method is applied using a 3 × 3 × 2 cluster model (Mg9O9) embedded in a 4 × 4 × 4 slab model. The calculated CO–Mg2+ distance is 248 pm, and the calculated CO frequency (blue) shift is 20 cm−1, 6 cm−1 larger than the experimental value. For the structure obtained, MP2 calculations with basis set extrapolation on a series of cluster models of increasing size are performed. Taking into account the difference in the periodic limit at the DFT + D level, 20.9 ± 0.7 kJ mol−1 is obtained as the estimate for the full periodic MP2 limit for the energy of CO desorption from the MgO(001) surface. CCSD(T) corrections are evaluated for the Mg9O9 cluster model using an augmented double-zeta basis set. Basis set extension effects are examined for smaller models. For a loading of Θ = 1/8, the estimated CCSD(T) value is 21.0 ± 1.0 kJ mol−1, which is 0.4 ± 1.0 kJ mol−1 larger than the (electronic) desorption energy derived in this study from TPD desorption barriers reported in the literature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...