Electronic spectroscopy of transient species in solid neon: the indene-motif polycyclic hydrocarbon cation family C9Hy+ (y = 7–9) and their neutrals†
Abstract
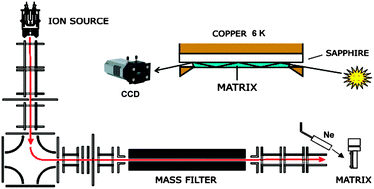
In this Perspective the development and application of a mass-selective matrix isolation approach, employed with success over the last two decades in the spectroscopic characterization of numerous ions and neutral reactive species, is illustrated with original data for hydrocarbon cations and neutrals with a six- and a five-membered carbon ring fused. The setup allows for the electronic and vibrational assessment of these isolated molecules and ions in the inert neon environment. The transient species of interest are chosen due to their astrophysical relevance, and the role they play in flames, plasmas, combustion, organic reactions and atmospheric chemistry. Electronic absorption and fluorescence spectra of indene-related polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives, C9Hy+ (y = 7–9) cations, are presented. The ions were produced in a discharge source and investigated by means of absorption and emission spectroscopies after selectively trapping them in 6 K neon matrices. Photoconversion between the two C9H8+ indenylium isomers and, upon irradiation, H2 loss from C9H9+ were observed. Corresponding neutral species C9Hy are identified by photobleaching the matrices containing the cations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...