Towards understanding the electronic structure of Fe-doped CeO2nanoparticles with X-ray spectroscopy
Abstract
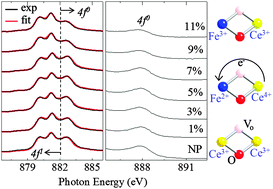
This study reports on the electronic structure of Fe-doped CeO2
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Physics, Tamkang University, Tamsui, Taiwan
E-mail:
clchang@mail.tku.edu.tw
b Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, California 94720, USA
c Department of Material Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei, Taiwan
d
National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center, Hsinchu, Taiwan
E-mail:
dong.cl@nsrrc.org.tw
e Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan
f Laboratoire de Physique des Solides, Université Paris Sud, CNRS UMR 8502, F-91405 Orsay, France
This study reports on the electronic structure of Fe-doped CeO2

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
W. Wang, S. Chen, P. Glans, J. Guo, R. Chen, K. Fong, C. Chen, A. Gloter, C. Chang, T. Chan, J. Chen, J. Lee and C. Dong, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 14701 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP52054D
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
