Z-DNA stabilization is dominated by the Hofmeister effect†
Abstract
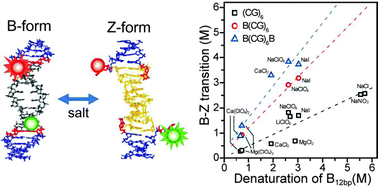
The manner in which Z-DNA is stabilized at high salt concentrations remains unclear. Here, we systematically examine the Z-DNA-stabilizing capabilities of different salts. The strong correlation between the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...