Predictions of particle size and lattice diffusion pathway requirements for sodium-ion anodes using η-Cu6Sn5 thin films as a model system†
Abstract
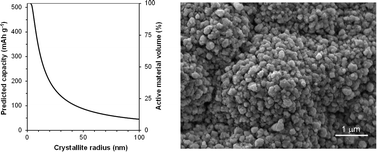
Geometrically well-defined Cu6Sn5 thin films were used as a model system to estimate the diffusion depth and diffusion pathway requirements of Na ions in alloy anodes. Cu6Sn5 anodes have an initial reversible capacity towards Li of 545 mA h g−1 (Li3.96Sn or 19.8 Li/Cu6Sn5), close to the theoretical 586 mA h g−1 (Li4.26Sn), and a very low initial irreversible capacity of 1.6 Li/Cu6Sn5 (Li0.32Sn). In contrast, the reaction with Na is limited with a reversible capacity of 160 mA h g−1 compared to the expected 516 mA h g−1 (Na3.75Sn).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...