Negligible water surface charge determined using Kelvin probe and total reflection X-ray fluorescence techniques
Abstract
The
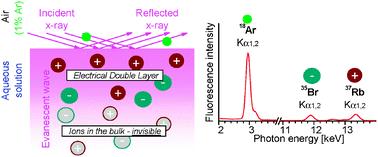
* Corresponding authors
a
N.N. Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics RAS, Kosygina 4, 119991 Moscow, Russia
E-mail:
shapoval@chph.ras.ru
Fax: +7 499 137 6130
Tel: +7 495 939 7345
b Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Research Campus Golm, 14424 Potsdam, Germany
c European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, BP-220, Grenoble, France
d Institute of Physics, Albert Ludwigs University, Hermann-Herder Straβe 3, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany
The

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
V. L. Shapovalov, H. Möhwald, O. V. Konovalov and V. Knecht, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15, 13991 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP51575C
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
