Functionalized 129Xe as a potential biosensor for membrane fluidity†
Abstract
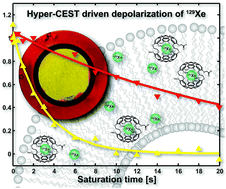
Using spin hyperpolarized xenon (129Xe) we investigate the impact of the local molecular environment on reversible host–guest interactions. We label Xe guest atoms that are temporarily bound to cryptophane-A hosts using the Hyper-CEST technique. By varying the length of the saturation pulse and utilizing an inverse Laplace transform we can determine depolarization times for the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...