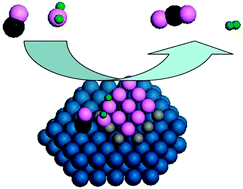
Reaction mechanism of WGS and PROX reactions catalyzed by Pt/oxidecatalysts revealed by an FeO(111)/Pt(111) inverse model catalyst
Abstract
We have employed
- This article is part of the themed collection: Interfacial Phenomena in (De)hydrogenation Reactions

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...