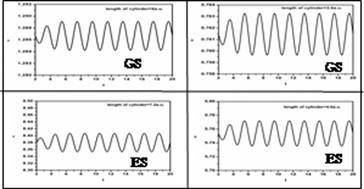
Time evolution of various reactivity parameters viz. hardness, electrophilicity, chemical potential, polarizability, etc. in a confined environment has been studied through quantum fluid density functional theory formalism during time dependent processes such as proton–molecule collisions and molecule–field interaction. A Dirichlet type boundary condition has been incorporated to confine the systems. Responses in the reactivity parameters of the diatomic molecules, in the dynamical context, in ground state as well as in excited state, have been reported. Harmonic spectra are generated in the cases of the external laser field interacting with H2 and N2 molecules.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...