Highly luminescent water-soluble quaternary Zn–Ag–In–S quantum dots for tumor cell-targeted imaging†
Abstract
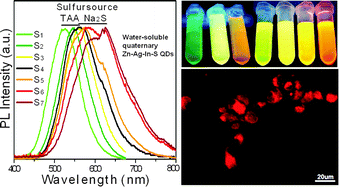
Exploring the synthesis and biomedical applications of biocompatible quantum dots (QDs) is currently one of the fastest growing fields of nanotechnology. Hence, in this work, we present a facile approach to produce water-soluble (cadmium-free) quaternary Zn–Ag–In–S (ZAIS) QDs. Their efficient photoluminescence (PL) emissions can be tuned widely in the range of 525–625 nm by controlling the size and composition of the QDs with the PL quantum yields (QYs) of 15–30%. These highly luminescent ZAIS QDs are less toxic due to the absence of highly toxic cadmium, and can be versatilely modified by a DHLA-PEG-based ligand. Importantly, after being modified by tumor cell-specific targeting ligands (e.g., folate and RGD peptide), the PEGylated quaternary QDs show potential applications in tumor cell imaging as a promising alternative for Cd-based QDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...