Association mechanisms of unsaturated C2 hydrocarbons with their cations: acetylene and ethylene†
Abstract
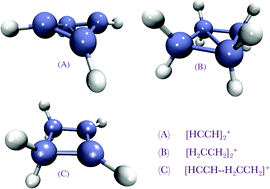
The ion–molecule association mechanism of acetylene and ethylene with their cations is investigated by ab initio quantum chemical methods to understand the structures, association energies, and the vibrational and electronic spectra of the products. Stable puckered cyclic isomers are found as the result of first forming less stable linear and bridge isomers. The puckered cyclic complexes are calculated to be strongly bound, by 87, 35 and 56 kcal mol−1 for acetylene–acetylene cation, ethylene–ethylene cation and acetylene–ethylene cation, respectively. These stable complexes may be intermediates that participate in further association reactions. There are no association barriers, and no significant inter-conversion barriers, so the initial linear and bridge encounter complexes are unlikely to be observable. However, the energy gap between the bridged and cyclic puckered isomers greatly differs from complex to complex: it is 44 kcal mol−1 in C4H4+, but only 6 kcal mol−1 in C4H8+. The accurate CCSD(T) calculations summarized above are also compared against less computationally expensive MP2 and density functional theory (DFT) calculations for structures, relative energies, and vibrational spectra. Calculated vibrational spectra are compared against available experiments for cyclobutadiene cation. Electronic spectra are also calculated using time-dependent DFT.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...