Quantitative estimate of the conductivity of a soggy sand electrolyte: example of (LiClO4, THF):SiO2
Abstract
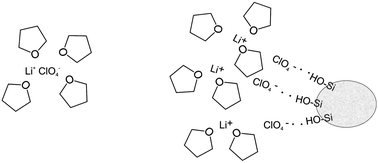
Electrolytes containing LiClO4/THF heterogeneously doped with SiO2 nanoparticles show AC conductivity enhancements even for very low SiO2 volume fractions. Based on the experimentally validated assumption that the silica particles adsorb preferentially anions and based on the availability of mass action constants for ion pairing in this special case we can quantitatively estimate local and overall conductivity and transference numbers. The found results are in satisfactory agreement with the measured experimental values.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...