Hydrogenated bilayer wurtzite SiC nanofilms: a two-dimensional bipolar magnetic semiconductor material
Abstract
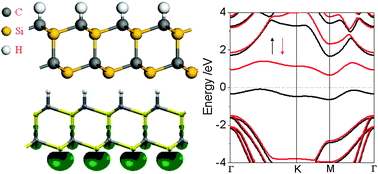
Recently, a new kind of spintronics material, bipolar magnetic semiconductors (BMS), has been proposed. The spin polarization of BMS can be conveniently controlled by a gate voltage, which makes it very attractive in device engineering. Now, the main challenge is finding more BMS materials. In this article, we propose that hydrogenated wurtzite SiC nanofilm is a two-dimensional BMS material. Its BMS character is very robust under the effect of strain, substrate or even a strong electric field. The proposed two-dimensional BMS material paves the way to use this promising new material in an integrated circuit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...