Synthesis and properties of four coordination polymers built from a semi-rigid tripod carboxylic acid†
Abstract
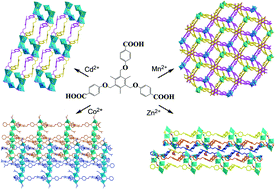
By using a semi-rigid multidentate carboxylate linker 4,4′,4′′-(((2,4,6-trimethylbenzene-1,3,5-triyl)tris(methylene))tris(oxy))tribenzoic acid (H3L), four coordination polymers, namely, [Cd3(L)2(H2O)4]·(guest) (1), [Mn3(L)2(DMF)2(H2O)2]·(guest) (2), [Co7(L)4(DMF)6(COOH)2]·(guest) (3), and [Zn3(L)2(DMF)2(H2O)3]·(guest) (4), were obtained and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric and photoluminescent studies. Compound 1 is a two-dimensional (2-D) hcb-type layered structure made of rare, interlocked double-layered honeycomb sheets. Compound 2 is a doubly-interpenetrating (3,6)-connected 3-D network, in which L and Mn3 act as triangle and trigonal prismatic nodes, respectively. Compound 3 has a (4,12)-connecting 3-D polycatenated network made of a rare four-ladder 2-D sheet, in which the Co7 cluster is considered as a 12-connecting node and the ligand L3− is a 3-connecting node. Similar to 1, compound 4 also possesses a 2-D hcb-type layered structure, but it is built from two interpenetrating single sheets. Compounds 1 and 4 exhibited strong blue photoluminescent emissions at room temperature upon excitation, owing to a ligand-centered excited state. The emission intensities of the two compounds varied upon contact with different solvents or analytes, exhibiting selective emission quenching responses towards nitroaromatics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...