CuO nanowire growth on Cu2O by in situ thermal oxidation in air†
Abstract
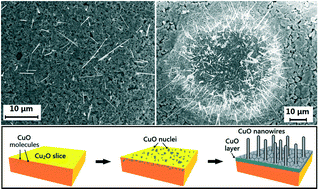
CuO nanowires were synthesized by in situ thermal oxidation of Cu2O for the first time in the temperature range of 300–750 °C in air. In this process, the effects of annealing temperature and growth time on the growth of CuO nanowires were investigated by SEM, XRD, EDS mapping and line-scan profile measurements. We found that the nucleation of CuO nanowires is a solid-state transformation process, and the nanowire length obeys a parabolic law with annealing time. The nanowire growth shows a diffusion-controlled behavior. Based on the above-mentioned study, the mechanism of the nucleation and growth of CuO nanowires from Cu2O is proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...