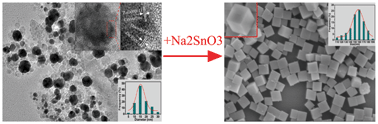
A environmental-friendly and simple method is developed to fabricate the nanostructured zinc hydroxystannate [ZnSn(OH)6, ZHS] based on laser ablation of Zn target in water and subsequent stannate reaction at a low temperature (5 °C) without any surfactants. The ZHS nanocubes with about 155 nm in edge length have been successfully produced. Such ZHS nanocubes are single crystalline with perovskite structure and enclosed by six external faces of {001} planes. They are unchanged in the shape after subsequent annealing at temperatures up to 800 °C. The amorphous nano-cubic zinc stannate (ZnSnO3), a multifunctional material, is thus produced by thermal decomposition of the pre-formed ZHS at 300–400 °C. Further experiments have revealed that the low reaction temperature and the laser ablation-induced ZnO colloids are crucial to formation of the ZHS nanocubes. This study is important to understand in detail the growth mechanism of the ZHS crystals, and also provides a green, simple and low-cost synthesis method for nanostructured ZHS and its decomposition products (ZnSnO3, Zn2SnO4 and SnO2, etc.).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...