Formation of low density hydrous iron oxide via conformal transformation of MIL-53(Fe)
Abstract
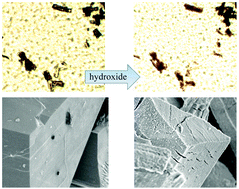
Hydrous iron oxide materials with a predefined shape, photo-electrochemical activity, low density (estimated to be 0.32 g cm−3), and high fractal porosity (BET ca. 117 m2 g−1) are formed via internal hydrolytic transformation of the crystalline metal–organic framework MIL-53(Fe) in dilute aqueous hydroxide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...