Chemical welding of binary nanoparticles: room temperature sintering of CuSe and In2S3nanoparticles for solution-processed CuInSxSe1−x solar cells†
Abstract
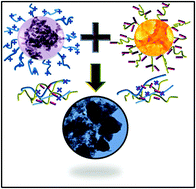
Chemical welding of oppositely charged dissimilar metal chalcogenide nanomaterials is reported to produce a quaternary metal chalcogenide. CuSe and In2S3

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...