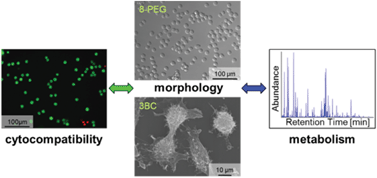
Cellular responses to various gels fabricated by photoinitiated crosslinking using acrylated linear and multi-arm poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based and poly(propylene glycol)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) precursors were investigated. While no protein adsorption and cell adhesion were observed on the hydrophilic PEG-based gels, protein adsorption and cell adhesion did occur on the more hydrophobic gel generated from the block copolymer precursor. Murine fibroblast viability on the poly(ethylene glycol)-based gels was studied in the course of 72 h and the results indicated no cytotoxicity. In a systematic study, extra- and intracellular metabolites of the murine fibroblasts cultured on these PEG-based gels were examined by GC-MS. Distinct intra- and extracellular changes in primary metabolism, namely amino acid metabolism, glycolysis and fatty acid metabolism, were observed. Cells cultured on the polymeric gels induced more intense intracellular changes in the metabolite profile by means of higher metabolite intensities with time in comparison to cells cultured on the reference substrate (tissue culture polystyrene). In contrast, extracellular changes of metabolite intensities were comparable.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...