Development of bilayer and trilayer nanofibrous/microfibrous scaffolds for regenerative medicine
Abstract
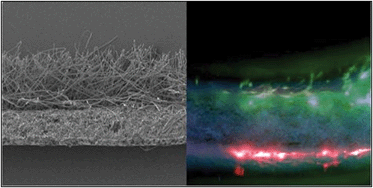
Many biomaterial scaffolds have been developed for use in tissue engineering usually for populating with a single cell-type. In this study we demonstrate the production of bilayer and trilayer nanofibrous/microfibrous biodegradable scaffolds suitable for the support, proliferation and yet segregation of different tissues – here used to separate soft tissue from bone forming tissue and keratinocytes from fibroblasts. Essentially we describe a nanofibre barrier membrane which is permeable to nutrients coupled with attached microfibers (either on one side or both sides) to support the proliferation of different cell types either side but prevents migration of cells across the barrier. Such membranes would be suitable for guided tissue regeneration in areas where one wishes to support both soft and hard tissues but keep them separated. We describe a sterile bilayer membrane electrospun from polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) (nanofibres) and polylactic acid (PLA) or poly ε-caprolactone (PCL) (microfibres) and a trilayer membrane electrospun in layers of PLA, PHBV, then PLA. These membranes are biocompatible, biodegradable and capable of supporting two different cell populations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...